Ask Dyna Blog
DNA Test Explained

Scientifically, the term DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid, and it carries the genetic information of an individual. It can tell what an individual inherits from his or her ancestors and what chances a person could pass down to his or her children.
General DNA Testing
DNA-based techniques have been used in many fields all over the world. DNA techniques are utilized in performing tests for health and wellness, paternity tests, or even forensics. However, the technique differs within each category. DNA carries a wealth of genetic information about medical illnesses, wellness, skincare, mental ability, behavioral traits, physical health, and more.
DNA testing, also known as genetic screening that is a medical test conducted to estimate or rule out the possibility of a person developing a genetic disorder. This test identifies the changes in genes, chromosomes, or proteins in the body. As of today, there are more than 77,000 genetic tests that can be conducted, and more are being developed [1].
Why is DNA Testing Important?
Through DNA testing, we are able to learn about the genetic conditions that run in our family even when we have no prior symptoms of specific conditions. DNA testing also helps us become more aware of any genetic conditions that we may pass down to our offspring [2]. With this knowledge, we can better prepare and understand treatment plans in advance for prevention or monitoring.
Blood Test Vs DNA Test
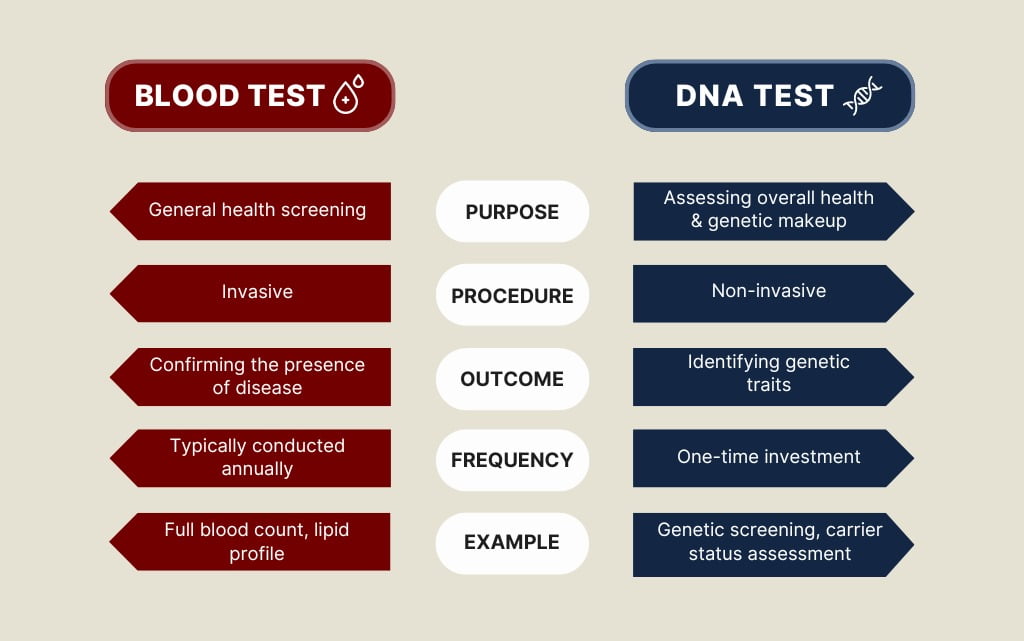
Many people find these two tests similar; however, both tests are different and serve their own purposes. One of the differences we can note from blood tests is that they require invasive techniques to obtain the blood sample. The primary purpose of the conducted blood test is for general health screening. Blood tests help to confirm and diagnose the onset of diseases and conditions [9]. Specifically, for this test, patients usually screen for complete blood count, basic metabolic panel, lipid profile, cardiac markers, and others [10].
In contrast, basic DNA tests mostly require non-invasive procedures such as buccal swab tests or saliva samples. A DNA test is performed to estimate the likelihood of a person having the risks of a disease [3]. These types of tests are more comprehensive as they help to trace back individual and family health history, their genes, and the possibility of outcome traits. For instance, familial hypercholesterolemia, cancer risk, or autosomal recessive traits.
4 Types of DNA Test
DNA testing is a vast field, encompassing over 70,000 genetic tests. One of the most commonly performed tests is genetic testing for health and wellness. The purpose of genetic testing is to identify changes in genes, chromosomes, or proteins.
Gene Test
Gene testing aims to identify genes that may increase the risk of a genetic disorder in an individual. It determines mutations in genes and analyzes an individual’s DNA as a whole [1].
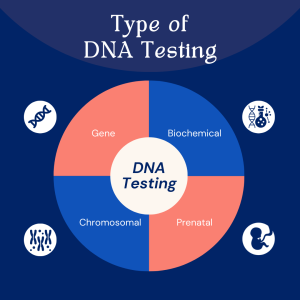
Chromosomal Genetic Test
This test examines changes in chromosomes, identifying patterns in either whole chromosomes or long lengths of DNA [1]. Significant genetic changes can indicate the risk of a genetic condition, such as an extra copy of a chromosome reflecting a syndrome.
Biochemical Genetic Test
Biochemical tests assess the activity levels of proteins and enzymes. Abnormalities in these proteins and enzymes indicate mutations in DNA, which can lead to genetic disorders [1].
Prenatal Testing
Prenatal testing detects abnormalities in genes and chromosomes in the developing fetus, enabling the identification of potential medical conditions the baby may be born with. However, it may only detect certain conditions. Nonetheless, this testing allows parents to monitor signs and symptoms of genetic conditions inherited from the family’s genetic history [4]. Prenatal DNA tests can be conducted during pregnancy to provide early exposure.
Prenatal testing encompasses two subtypes: screening tests and diagnostic tests. The major difference lies in the fact that screening tests only provide limited information about the risk of a baby having a certain disorder, while diagnostic tests confirm and provide more definitive information about the baby’s medical condition.
In addition to prenatal testing, DNA paternity testing is one of the most common tests performed. Paternity tests determine the biological relation between a child and the father with extremely high accuracy. Such tests can indicate, with a precision of 99.9%, whether a man is not the biological father of an individual [7]. Other common tests include diagnostic and carrier testing [1].
Accuracy of DNA Testing (Genetic Screening)
In genetic testing, microarray-based DNA testing technology is commonly used. This technology is highly accurate, with sensitivity and specificity close to 99%. It can detect genetic mutations and analyze a large number of genetic markers, allowing for comprehensive assessment of an individual’s genetic profile [8]. A comparison study method has been performed to test the accuracy and consistency of the analysis. The study demonstrated an accuracy of >99% for all samples analyzed, indicating that the method is highly reliable for screening genetic tests [8].
In Malaysia, DynaDNA is one of the best DNA screening tests for checking health and wellness. DynaDNA offers a complete 10-profile screening test inclusive of nutrigenomics, lifestyle and health risk assessment, carrier status, drug sensitivity test, and many more. It provides a clinical-grade test report and personalized recommendations based on individual needs.
